Executive Summary
As global urbanization accelerates, the impermeability of city surfaces has reached critical levels, rendering traditional “pipe-and-pond” drainage methods obsolete. For civil engineers, architects, and municipal planners, the challenge has shifted from rapid conveyance to decentralized volume management.
This technical guide provides a comprehensive analysis of Underground Modular Polypropylene (PP) Stormwater Storage Tanks. We will dissect the structural mechanics, hydraulic advantages, regulatory compliance (including CIRIA C737 and Eurocodes), and the installation economics that make modular systems the superior choice over concrete and aggregate solutions for high-load commercial and industrial applications.
1. The Hydrological Imperative: Why Detention is No Longer Optional
The fundamental driver for the adoption of stormwater storage tanks is the stringent regulation of Runoff Volume and Peak Flow Rates.
1.1 The Failure of Conventional Drainage
Historically, urban drainage relied on combining storm and sanitary sewers or simply channeling water rapidly to the nearest watercourse. However, climate change data indicates a significant increase in high-intensity, short-duration rainfall events.
-
Hydraulic Overload: Old municipal pipes cannot handle the increased velocity and volume, leading to Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs) and urban flooding.
-
Regulatory Caps: Regulations such as the US EPA’s NPDES (National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System) and the UK’s Flood and Water Management Act now require “Pre-development Hydrology.” This means post-construction runoff rates cannot exceed the natural greenfield runoff rates.
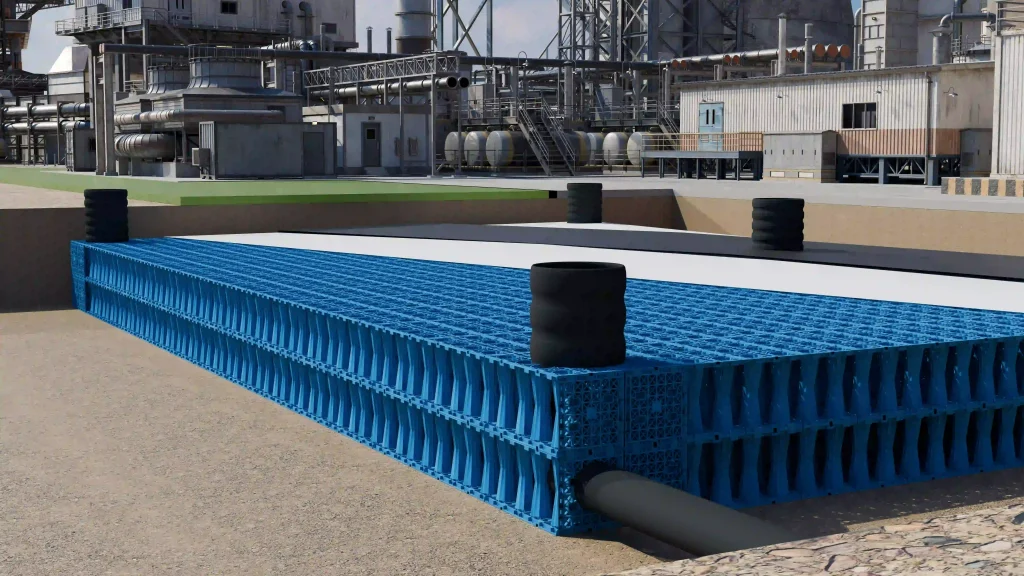
1.2 The Role of Attenuation vs. Infiltration
Engineered storage tanks serve two distinct hydraulic functions based on soil permeability (Geotechnical Baseline Report data):
-
Attenuation (Detention): In clay or impermeable soils, the tank temporarily stores peak flow water and releases it slowly via a Flow Control Device (Vortex Valve or Orifice Plate).
-
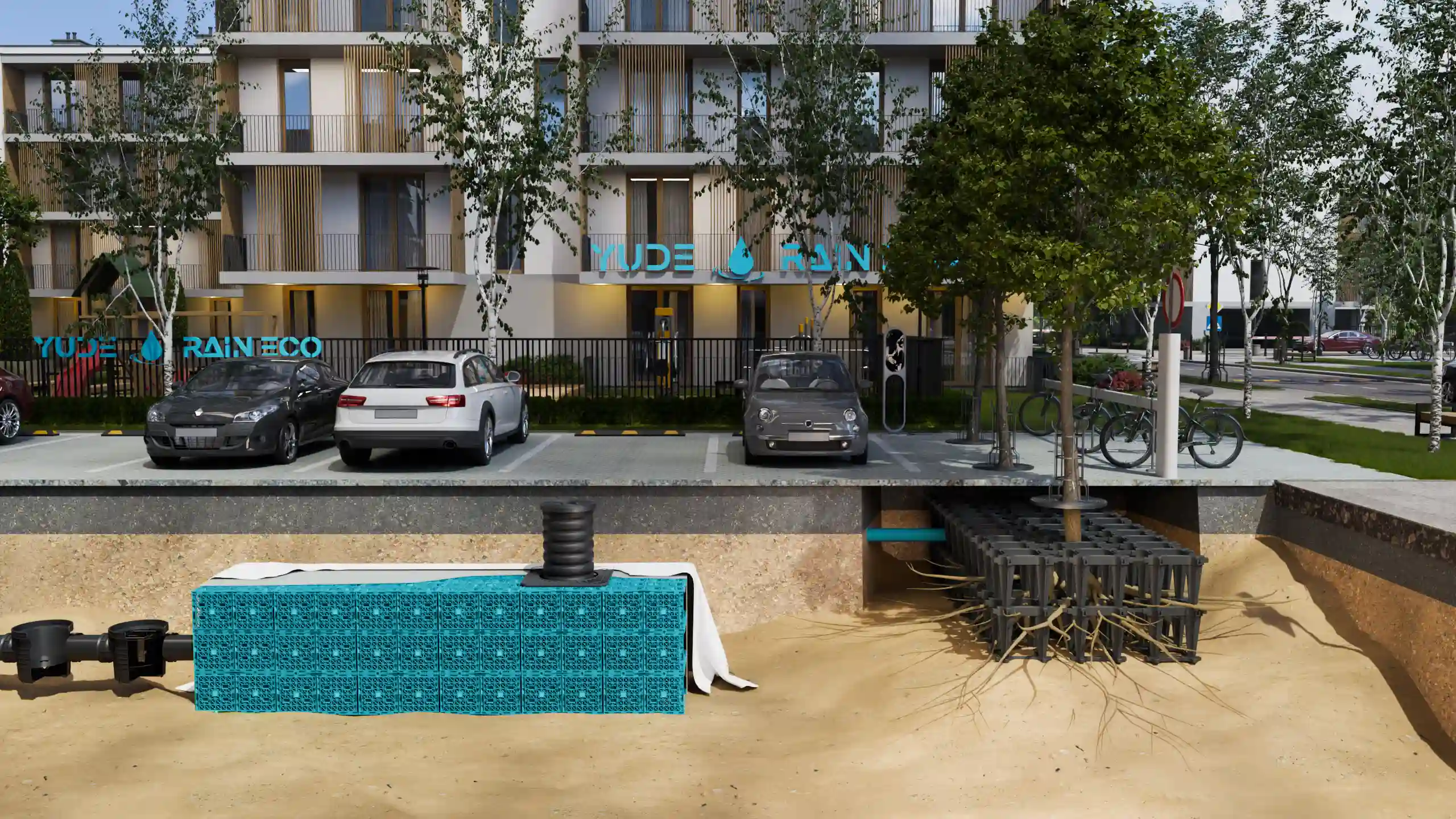
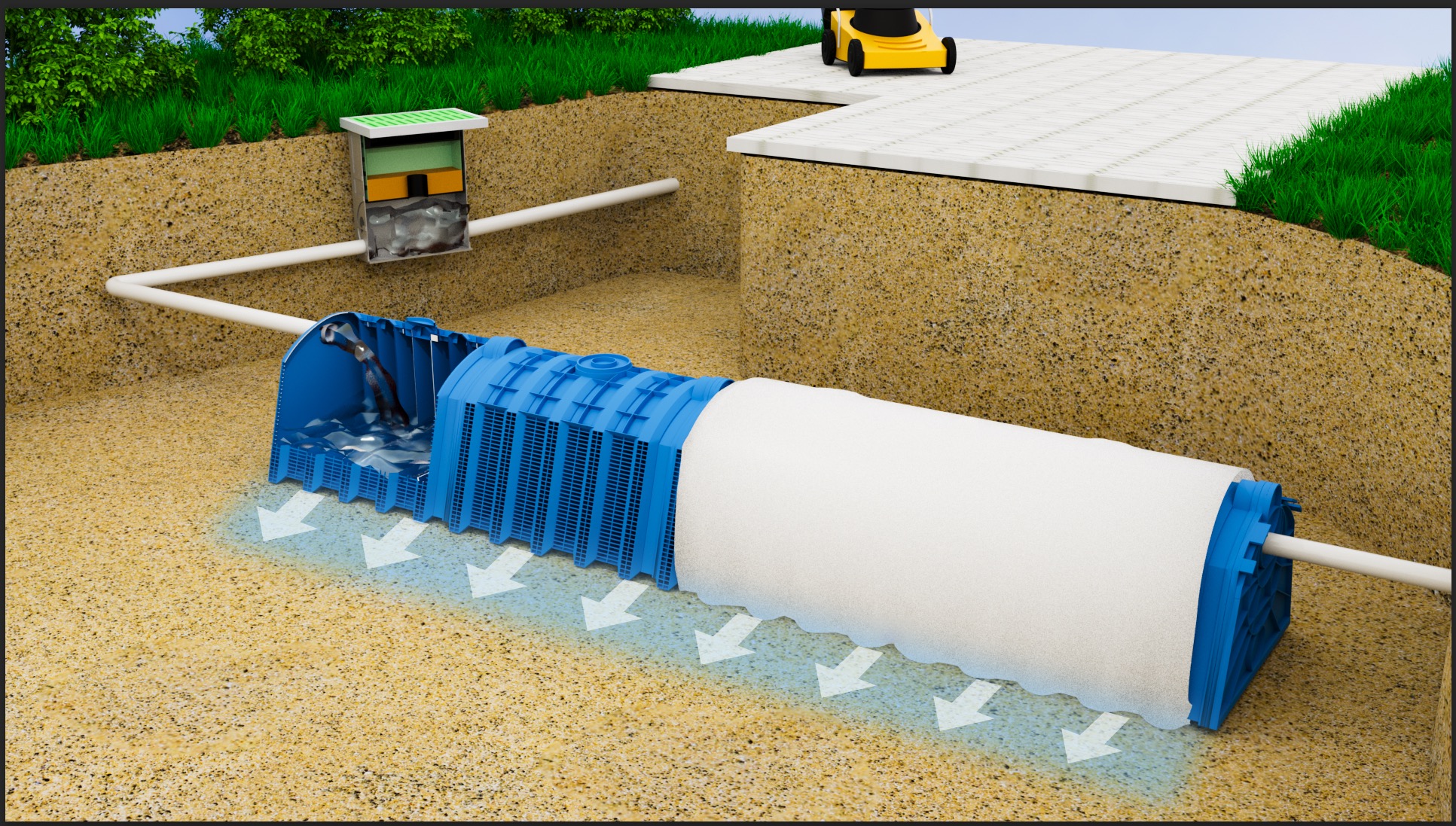
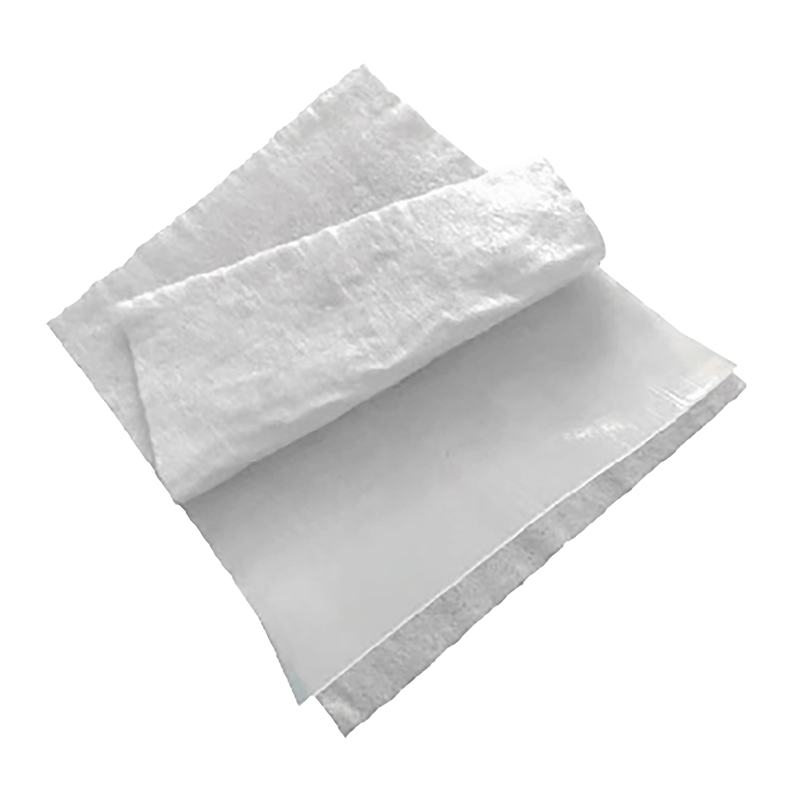
Infiltration (Soakaway): In sandy or permeable soils, the tank is wrapped in a permeable geotextile, allowing water to recharge the groundwater table, aligning with LID (Low Impact Development) principles.
2. Comparative Analysis: Modular PP Units vs. Traditional Materials
When specifying a stormwater solution, the engineer must evaluate the Void Ratio (Porosity), as this directly dictates excavation volume and project cost.
2.1 The Void Ratio Mathematics
The efficiency of a storage medium is defined by how much “air” it provides per cubic meter of material.
-
Traditional Aggregate (Stone/Gravel):
-
Void Ratio: Typically 30% to 40%.
-
Calculation: To store 100 m³ of water, you need to excavate and fill a volume of ~250 m³ to 333 m³.
-
Impact: Massive excavation costs, high soil disposal fees, and hundreds of truck movements for aggregate delivery.
-
-
Concrete Cisterns:
-
Void Ratio: High (internal), but heavy wall thickness reduces overall footprint efficiency.
-
Drawback: Requires heavy lifting cranes, long curing times (28 days for full strength), and is prone to cracking under differential settlement.
-
-
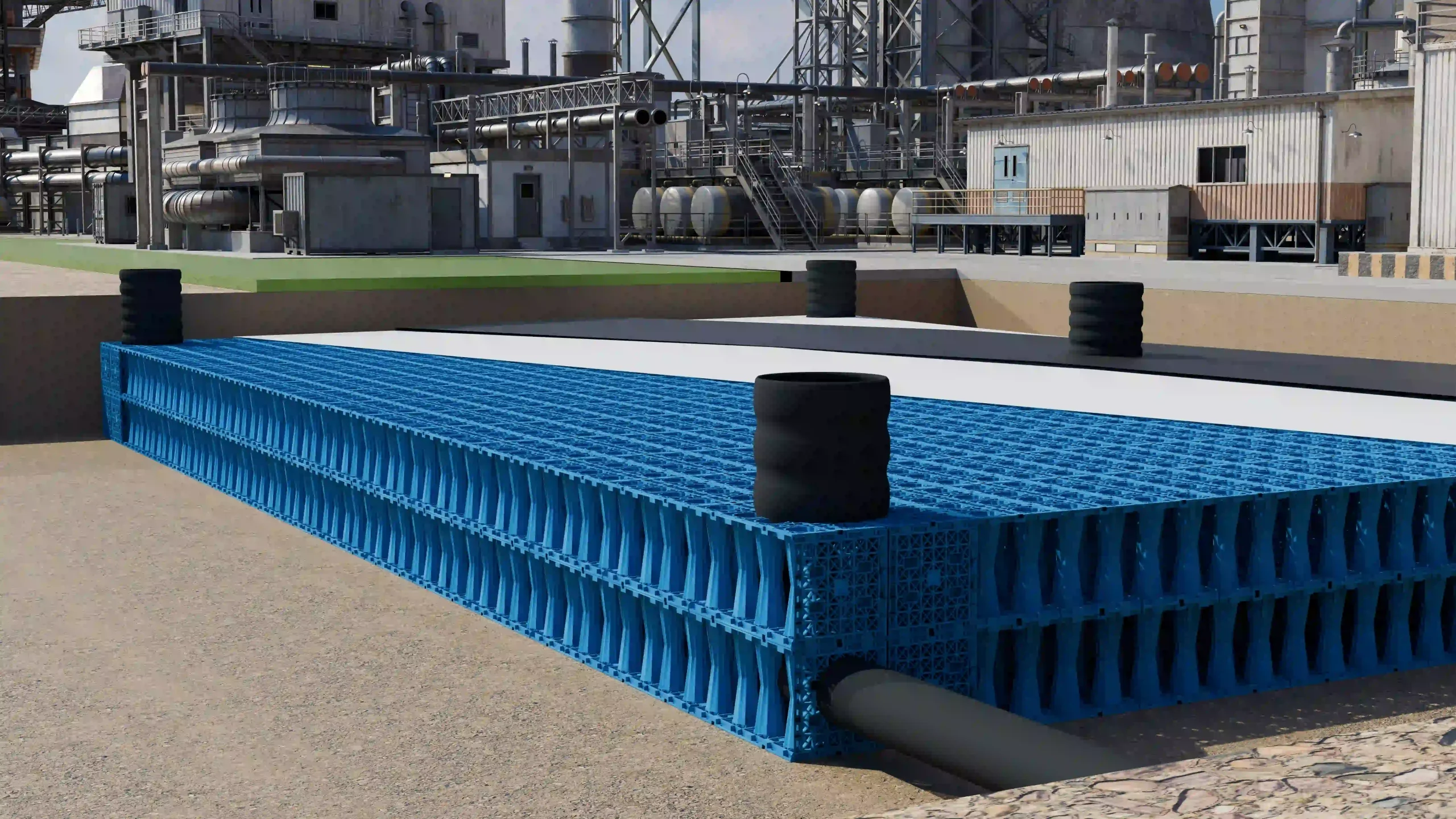
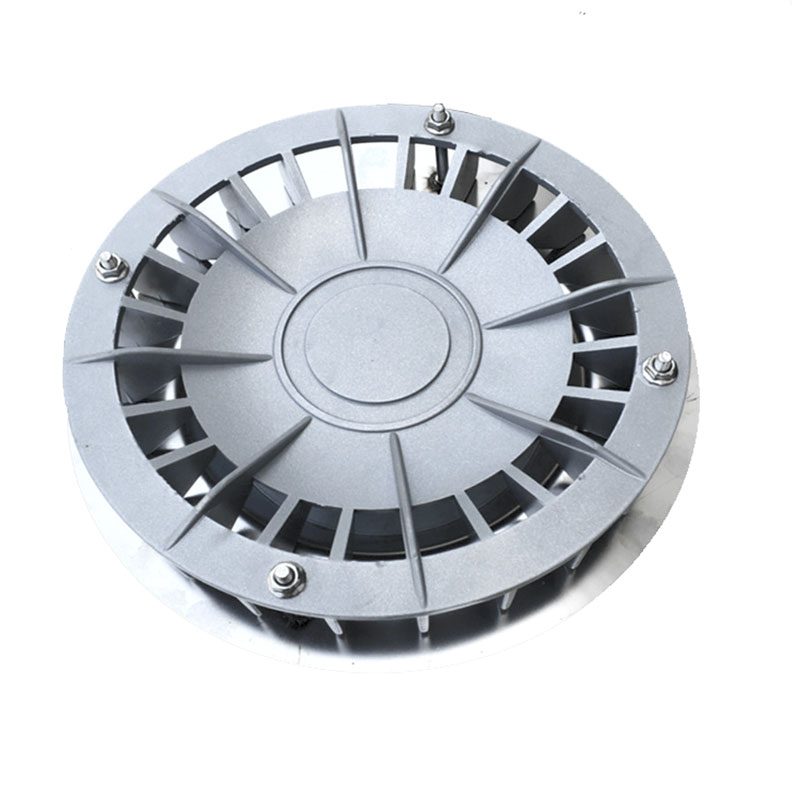
Yude Rain Eco Modular PP Tanks:
-
Void Ratio: 95% to 97%.
-
Calculation: To store 100 m³ of water, you only need an excavation of ~105 m³.
-
Advantage: This represents a 58% to 68% reduction in earthworks compared to gravel. For a project in a dense urban center like London, New York, or Dubai, this spatial efficiency is the deciding factor.
-
3. Structural Mechanics: Designing for Load and Longevity
One of the most common questions from structural engineers is: “Can plastic really support the load of a 40-ton fire truck?” The answer lies in the Geometry and Material Science of the modules.
3.1 Material Science: Virgin vs. Recycled Polypropylene
The longevity of an underground structure is determined by its resistance to Creep (deformation under constant load over time).
-
Virgin PP: Yude Rain Eco utilizes high-grade, virgin Polypropylene. This material exhibits a consistent Creep Modulus, ensuring that the tank will not collapse or deform significantly over a 50-year design life.
-
Recycled Mixed Plastics: While cheaper, inconsistent polymers can suffer from “Stress Cracking” and unpredictable creep behavior, risking catastrophic surface subsidence.
3.2 Understanding Load Ratings: SLS and ULS
Designing a modular tank system requires adherence to strict safety factors, often referenced in CIRIA C737 (Structural design of modular geocellular drainage tanks).
-
SLS (Serviceability Limit State): This measures the deflection of the tank under normal daily loads. The industry standard typically limits deflection to a specific percentage of the height (e.g., <1%) to ensure the road surface above does not crack.
-
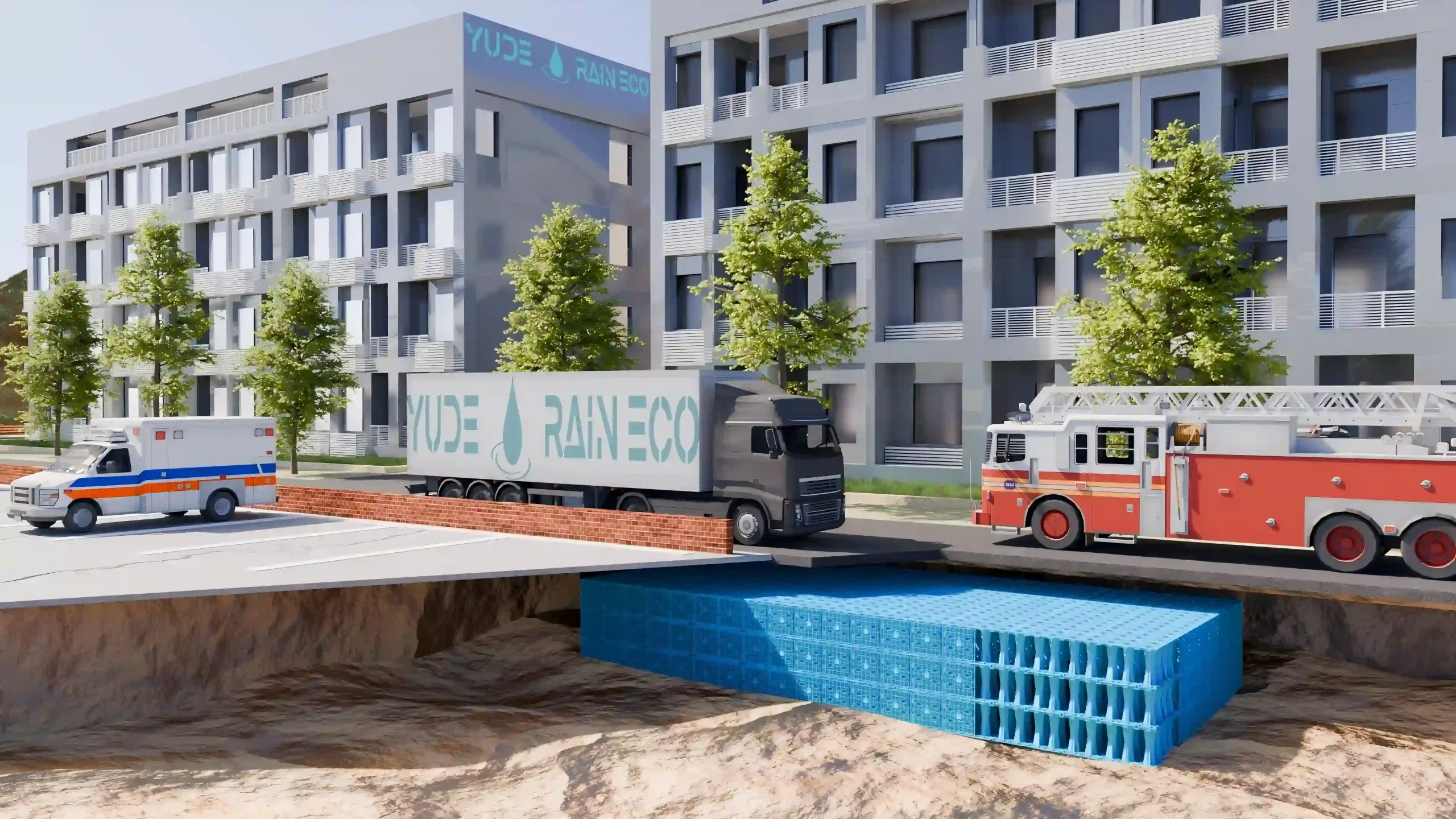
ULS (Ultimate Limit State): This is the breaking point. Yude Rain Eco’s heavy-duty modules (e.g., 60T Series) are tested to withstand vertical loads exceeding 600 kN/m².
-
Application: This allows installation under HGV loading bays, fire access routes, and high-traffic parking lots, provided the minimum cover depth (usually 0.8m – 1.0m) and engineering backfill specifications are met.
-
3.3 Lateral Earth Pressure
It is not just the weight from above (Vertical Load) that matters; the tank must also resist the Lateral Earth Pressure from the surrounding soil. Our specific “Columnar” or “Honeycomb” internal structures are designed to distribute these side loads evenly, preventing sidewall buckling—a critical feature for deep burial applications (>2.5m depth).

Technical Comparison: StormBreaker® vs. Concrete vs. HDPE Underground Tanks
| Technical Criteria | Yude StormBreaker® (PP Modular) | Concrete Underground Tanks | HDPE Underground Tanks (Pipe/Arch) |
| Material Composition | Virgin Polypropylene (PP)
(High creep resistance & structural memory) |
Reinforced Concrete
(Rigid, heavy, susceptible to chemical attack) |
High-Density Polyethylene
(Flexible, requires structural backfill support) |
| System Void Ratio | 95% – 97%
(Maximum storage volume per m³ of excavation) |
~85% – 90%
(Thick walls and pillars reduce effective capacity) |
~35% – 60%
(System volume is significantly reduced by required stone backfill) |
| Excavation Footprint | Minimal
(Highly efficient; requires less earthwork) |
High
(Requires larger footprint for wall thickness) |
Extensive
(Requires wide spacing between pipes for structural fill) |
| Load Bearing Capacity | Up to 600 kN/m² (60T)
(Engineered for HGV & Fire Access loading) |
Very High
(Strong, but prone to cracking under differential settlement) |
Variable (H-20/H-25)
(Heavily dependent on the compaction quality of stone backfill) |
| Installation Speed | Rapid Assembly
(Manual installation; ~400m³/day with 4 workers) |
Slow
(Requires formwork, heavy lifting, and 28-day curing time) |
Moderate
(Pipe connections are fast, but stone backfilling is slow) |
| Transport Logistics | Stackable / Nestable
(1 truck of modules ≈ 50 trucks of gravel/pipe) |
Complex
(Heavy precast sections require specialized heavy haulage) |
Inefficient
(Transporting “air”; bulky pipes fill trucks quickly) |
| Design Flexibility | 100% Modular
(Adapts to irregular site shapes and existing utilities) |
Rigid / Fixed
(Rectangular shapes only; difficult to retrofit) |
Linear Only
(Limited to long trenches; poor area utilization) |
| Maintenance Access | Integrated Inspection Tunnels
(Fully compatible with CCTV & Jetting) |
Confined Space Entry
(Hazardous; requires personnel to enter the tank) |
Limited
(Access is typically limited to manholes; difficult to clean) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent
(Resistant to acids, alkalis, and road salts) |
Moderate
(Vulnerable to sulfate attack and acidic soils) |
Excellent
(Resistant to most chemicals, similar to PP) |
| Lifecycle Sustainability | Low Carbon / Recyclable
(100% Recyclable; Low transport emissions) |
High Carbon Footprint
(Cement production is a major CO₂ emitter) |
Moderate
(Recyclable material, but high excavation carbon cost) |
4. Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
For our global clients, Yude Rain Eco ensures our systems align with the most rigorous international standards.
4.1 Europe & UK: CIRIA C737 & BS EN 17152-1
-
CIRIA C737: We follow the rigorous testing protocols for short-term and long-term compressive strength. This standard replaced the older CIRIA C680, introducing more conservative safety factors for plastic geocellular units.
-
EN 17152-1: Plastics piping systems for non-pressure underground conveyance and storage of non-potable water. Our compliance ensures that our boxes meet the European benchmark for material quality and durability.
4.2 USA: ASTM & AASHTO
-
Load Ratings: Our systems are engineered to accommodate AASHTO H-20 and H-25 highway loading standards when installed with the correct cover and backfill.
-
ASTM F2418/F2787: While specifically for corrugated chambers, we utilize similar testing methodologies to verify structural integrity and joint connections.
5. Installation Methodologies & Site Logistics
The “Time-to-Market” value proposition of modular tanks is unbeatable.
5.1 The “Lego-Style” Assembly
Unlike concrete pouring which is weather-dependent, modular tanks are pre-manufactured and snap-assembled on site.
-
Speed: A team of 4 workers can install approximately 300 m³ to 500 m³ per day.
-
Safety: No heavy cranes are required inside the excavation pit, significantly reducing Health & Safety risks.
5.2 The Critical Role of Backfill
The structural strength of a modular system is a composite of the plastic unit and the surrounding soil (Soil-Structure Interaction).
-
Sidefill: We specify free-draining, angular stone (e.g., 20mm clean stone) compacted in layers. This material “locks” into the sides of the modules, transferring vertical loads into the surrounding ground.
-
Top Layers: A Geogrid layer is often recommended for low-cover applications to prevent differential settlement and distribute wheel point loads.
6. Maintenance and Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
Sustainability is not just about the installation; it is about the operational lifecycle.
6.1 Silt Management: The Achilles Heel
A poorly designed system will silt up within 5 years, reducing capacity. Yude Rain Eco Solution: We integrate Sediment/Silt Traps and pre-filtration units (upstream hydrodynamic separators).
-
Inspectability: Our tank designs include designated Inspection Tunnels that align with access ports.
-
Maintenance Protocol: Facilities management can use standard CCTV drain cameras and high-pressure jetting (at low psi) to flush debris from the “sediment tunnel” without disturbing the main storage body.
6.2 Environmental Impact (Carbon Footprint)
-
Recyclability: PP is 100% recyclable at the end of its life.
-
Transport Carbon: Because the modules are lightweight and stackable (or nestable), one truck of Yude Rain Eco modules carries the equivalent storage volume of 50 trucks of gravel. This drastically reduces the project’s Scope 3 Carbon Emissions.
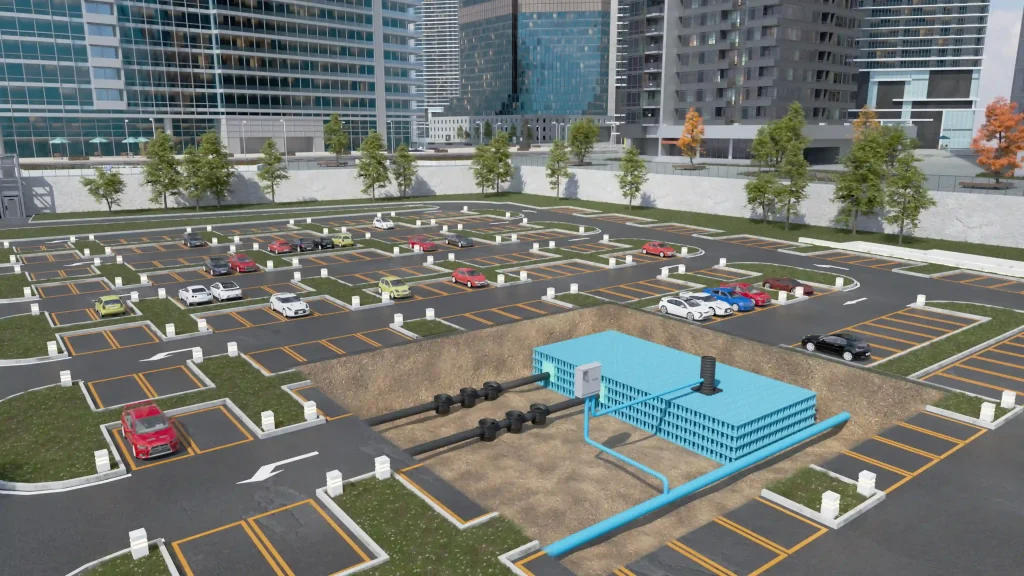
7. Case Study Application: Industrial Logistics Park
-
Scenario: A 50,000 m² Logistics Center in a heavy rainfall zone.
-
Requirement: Manage a 1-in-100-year storm event + 40% climate change allowance.
-
Solution: Installation of a 2,500 m³ Yude Rain Eco Attenuation System under the HGV turning circle.
-
Result:
-
Saved 4 weeks on the construction schedule compared to concrete.
-
Achieved full compliance with local discharge limits (5 Liters/second/hectare).
-
Provided a structurally sound, inspectable asset for the property owner.
-
Conclusion: Partnering for Resilience
The era of “bury and forget” is over. Modern stormwater management requires precision engineering, verified data, and compliant materials. Yude Rain Eco stands at the intersection of hydraulic efficiency and structural safety.
Whether you are designing a sponge city project, a commercial plaza, or an industrial facility, our engineering team is ready to support you with hydraulic calculations, CAD drawings, and installation guidance.
Don’t compromise on your infrastructure. Choose the experts.
Ready to Optimize Your Stormwater Design?
Don’t let drainage challenges delay your project. Whether you need a simple soakaway calculation or a complex attenuation design for a 50,000m² industrial park, Yude Rain Eco’s engineering team is here to help.
We provide FREE preliminary hydraulic designs, CAD layout drawings, and bill of quantities (BOQ) estimates to help you win your bid.
[Get My Free Design Consultation & Quote]
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can Yude Rain Eco modular tanks be installed under heavy-traffic roads?
A: Yes. Our High-Load Series (e.g., 60T/m² Ultimate Strength) is specifically engineered for trafficked areas, including HGV loading bays, fire access roads, and car parks. When installed with the correct minimum cover (typically 800mm-1000mm) and engineered backfill, they meet the structural requirements equivalent to AASHTO H-20 / H-25 loading standards.
Q2: What is the design life of your PP stormwater modules?
A: Yude Rain Eco modules are manufactured from high-quality Virgin Polypropylene (PP), which is resistant to naturally occurring chemicals, bacterial attack, and acid/alkali soil conditions. When installed according to our guidelines, the system has a design life expectancy exceeding 50 years, making it a permanent asset for infrastructure projects.
Q3: How do you prevent the tanks from silting up over time?
A: Maintenance is designed into our system. We recommend installing a pre-treatment device (like a silt trap or hydrodynamic separator) upstream. Additionally, our tanks feature dedicated Inspection and Maintenance Tunnels compatible with standard CCTV cameras and jetting equipment, allowing for easy sediment removal without excavation.
Q4: What are the minimum and maximum burial depths?
A: Burial depth depends on the specific module model and soil conditions. Generally:
-
Minimum Cover: 0.5m for landscaped areas; 0.8m – 1.0m for trafficked areas (to prevent point-load damage).
-
Maximum Depth: Our reinforced modules can be buried up to 4.0m – 5.0m deep, provided lateral earth pressures are accounted for in the design. Always consult our technical team for deep-burial calculations.
Q5: Are your tanks compatible with geomembranes for watertight applications?
A: Absolutely. For Attenuation (Detention) applications where water must be held and released slowly, the entire tank array is wrapped in an impermeable Geomembrane (typically HDPE or EPDM) and protected by a heavy-duty Geotextile. We can supply pre-fabricated membrane liners for faster installation.















